Blockchain is a digitized, verifiable, decentralized technology that’s used to capture and verify transactions between two parties in a provable and permanent way. Due to its decentralized nature, multiple stakeholders use the blockchain to efficiently record, report on and track verified interactions.
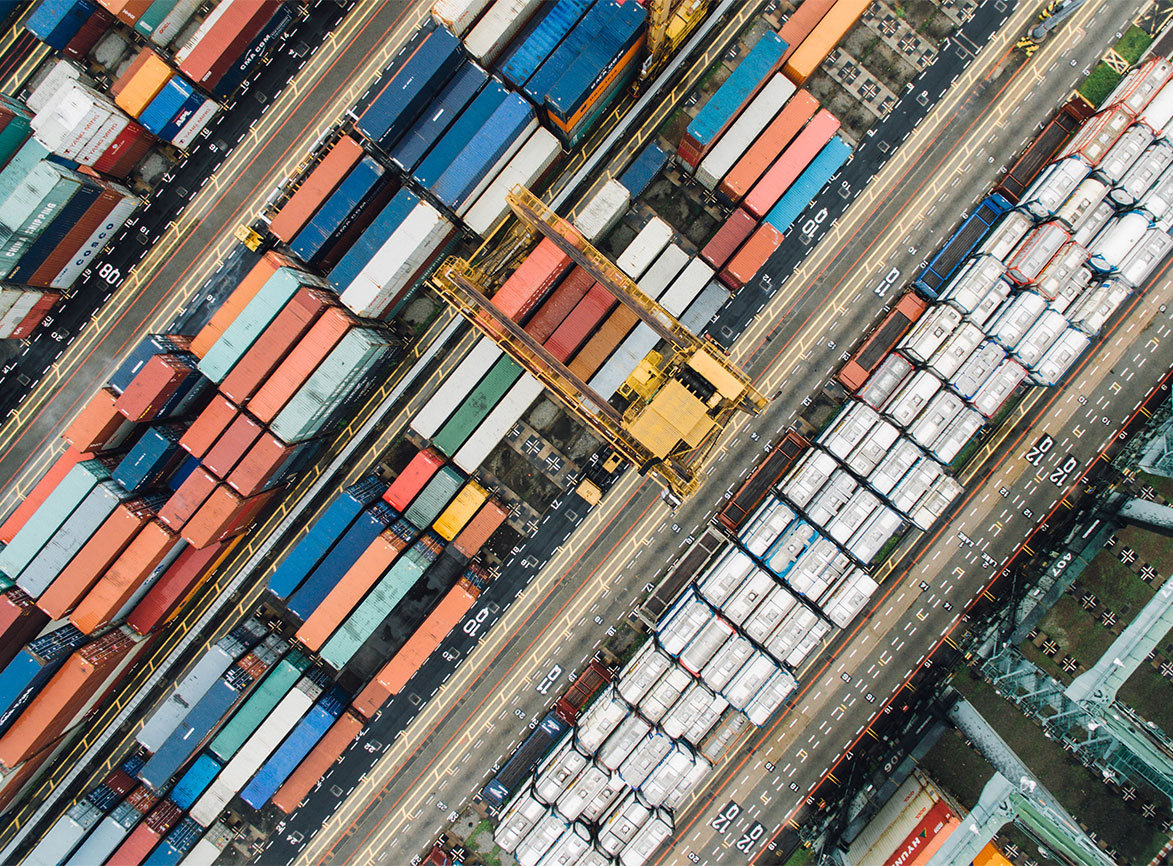
Blockchain technology works with supply chain management (SCM) to provide an immutable ledger for keeping and transferring records. This makes it easier to track and manage the sourcing, manufacture, storage, transfer and distribution of raw ingredients, materials and products.
When combined with other technologies like artificial intelligence or the Internet of Things, the blockchain provides significant benefits for SCM. These include transparency and access for supply chain data, rapid troubleshooting of inefficiencies and waste, real-time tracking and authentication and faster movement of goods through the supply chain.
How Blockchain Relates to the Supply Chain
Blockchain technology is easily integrated into supply chain management in several areas.
Capture and Verify the Quantity and Handover of Materials and Products
The blockchain is an excellent way to record the quantity, movement, location and transfer of materials, raw ingredients and finished products. A “smart contract” stored on the supply chain captures various data about goods that can be verified by all stakeholders, providing transparent information to all parties.
Track Where Goods Are Located at Any Time
IoT tracking devices are attached to goods, shipments and containers and provide real-time updates on their location. Geographical and other information can be captured in the blockchain to provide verified location data at all times for tracking goods. This helps to optimize the movement of goods and can speed up sourcing, transfer, manufacturing and distribution.
Understand Where Goods Are Sourced From
The complexity of traditional supply chains makes it difficult to understand the history and origin of raw materials, ingredients and finished products. Organizations in the blockchain can record the sourcing and transfer of goods so SCM understands the history of specific products and ensures quality and ethical standards are met.
Make Administration Much Easier
The verification and tracking of goods means SCM understands when and where goods have been received which helps to optimize administration. This speeds up payments, manufacturing processes, transfer and further distribution of goods. Additionally, documents like contracts, shipping notes, barcodes, digital tags and more are recorded on the blockchain for improved management.
Why Blockchain Matters to the Supply Chain
Blockchain technology delivers several benefits for efficient SCM.
- The blockchain introduces transparency to the supply chain. Open, real-time access to data means SCM can query, verify, report on and optimize the sourcing, transfer, manufacture and distribution of goods, wherever they are.
- If goods are lost or delayed, blockchain technology verifies their history and progress. This makes it easier to understand potential issues and bottlenecks, resulting in greater efficiencies, reduced waste, fewer delays and easier auditing of products.
- Understanding the progress of goods means SCM can optimize and streamline manufacturing and distribution. A manufacturer can plan exactly when they will receive materials and work that into their schedules, resulting in faster turnaround. Logistics businesses can use blockchain reporting to make distribution faster and easier.
How Blume Global is transforming freight audit and pay with blockchain-enabled Blume Finance.
The Challenges of Using Blockchain in the Supply Chain
The main challenge with using blockchain in the supply chain is ensuring stakeholders and organizations record data consistently and accurately. It’s vital that SCM requires all parties to use the same integrated blockchain platform.
Additionally, the complexity of blockchain can be a challenge for many stakeholders. Ideally, blockchain integration should be seamless and transparent, and be deployed through easy-to-use platforms for maximum adoption.
Use Cases for Blockchain in Retail and Manufacturing Supply Chains
- Manufacturers use real-time tracking of materials wherever they are in the supply chain to prepare to receive the materials and manufacture them quickly. This is an excellent way to optimize “Just in Time” manufacturing.
- Logistics businesses track and verify the distribution and final delivery of goods by tracking delivery times and customer signatures for verification.
- SCM capture contract agreements on the supply chain and arrange for digital signing so everyone is working to commonly agreed guidelines.
- Payment and escrow providers understand exactly when goods have arrived at specific organizations or destinations and hold payment until receipt has been verified by all parties.
- Insurers and auditors track the history and location of goods in case of products being delayed, going missing or getting damaged.
- SCM optimizes the flow of goods through the supply chain by extracting data and using machine learning and AI to streamline operations.
contact us
Contact Us